Inclinometers
An inclinometer is a system for measuring displacements across a reference line in ground and structures.
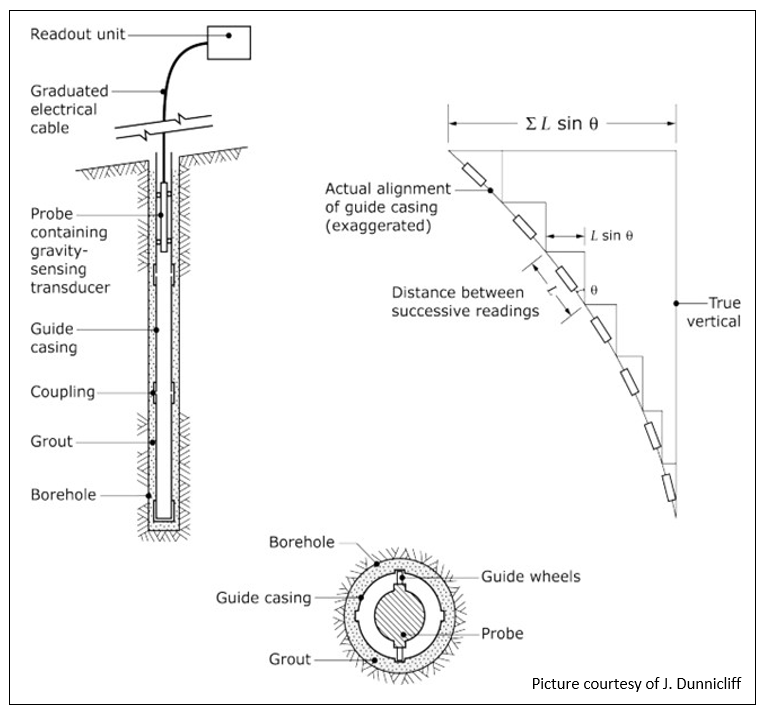
The measuring device contains tilt sensors inside a rigid tube. The tilt sensors measure the angles that the tube makes with the reference line in orthogonal directions. The relative deviation between the ends of the tube is calculated using trigonometry and the displacement is calculated by subtracting one measurement of deviation from another.
The measuring device is placed inside a guide tube (known as an inclinometer casing) that is installed along the reference line in the ground or structure where the measurement is required. The guide tube may have internal grooves (normally four at 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees to the anticipated direction of displacement). The guide tube is normally installed inside a borehole (or a reservation tube in a structure) and the space between the borehole and the ground (or reservation tube) is filled with a cement/bentonite grout.
Measurements can be made by running a measuring device along the grooves to measure the deviation at intervals equal to the length of the measuring device. This is known as a Probe Inclinometer Device. Alternatively measuring devices can be connected to each other and left inside the guide tube. This is known as an In-place Inclinometer System.
Typical applications for inclinometer systems (locations shown in red)